Special Procedures in Radiology
Good evening readers, today we are talking about special procedures performed in a radology department for various kind of findings. This article specifically deals with definitions of different procedures performed by using of X-ray machine, CT Scanner, etc radiological modalities.
As we knew routine x-rays are not enough when we have to find the working of various body organs like kidney, or we want to find unnatural internal body structure like in case of a sinus, as routine X-ray exams provide limited finding. To overcome this limitation and to provide proper diagnosis, we perform some special procedures with the help of contrast medium as a highlighter, if we talk more simply. Special procedures can be performed by using of an X-ray machine or CT sanner or by other modality, according to need.
Following are the list of some most commonly performed special procedures in descending order (on the basis of number of cases performed Globally).
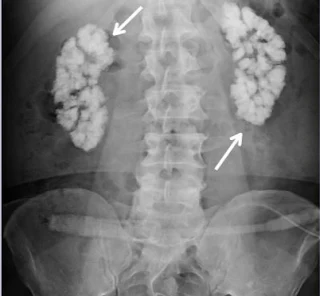
1. Intravenous Pyelography.
It is also called, Intravenous Urography and abbreviated as IVP. It is a radiographic examination of urinary tract including renal parenchyma calyx and pelvis after intravenous injection of contrast medium.
2. Micturating Cystourethrography.
It is a radiological contrast medium investigation use mainly for urethra for any obstruction or stress. It is abbreviated as MCU.
3. Retrograde Urethrography.
It is most of the time performed with Micturating Cystourethrography for proper diagnosis of urethra. It is a radiological contrast medium investigation of urethra to rule out structure, diverticulae and false passage of male urethra. It is abbreviated as RGU.
4. Hysterosalphangiography.
It is a radiographic investigation to study the anatomy and physiology of uterus and fallopian tube in female patients by using a contrast medium throught vagina. It is abbreviated as HSG.
5. Barium Swallow.
It is a radiographic contrast medium investigation to rule out diagnostic findings of oesophagus from oral cavity upto the fundus of the stomach. Barium sulphate paste is used as a contrast medium.
6. Barium Meal.
It is the radiological contrast medium investigation of Stomach, Duodenum and proximal Jejenum. Oesophagus is also included, depends on the need and in this case it will call Barium Swallow & Meal. Thick Barium sulphate suspension is used as contrast medium.
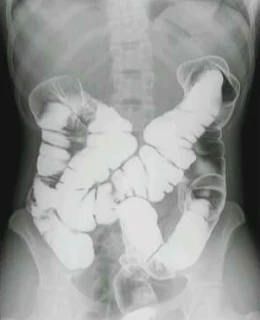
7. Barium Meal Follow Through.
It is a radiological contrast medium investigation, use to demonstrate whole of small bowel upto the illeo-ceacal junction. It is a part of barium study. It use suspension of barium sulphate solution as contrast medium. It is abbreviated as BMFT.
8. Barium Enema.
It is last barium study. It is a radiological contrast medium investigation which demonstrates whole large Bowel from rectum upto the illeo-ceacal junction. Don't confused with reversal order of digestive tract in definition. This exam in perform through rectum by pushing Barium sulphate suspension as contrast medium in it.
9. Post-operative Cholangiography.
It is also known by, T-tube Cholangiography. It is a radiographic contrast media investigation, used to study the biliary tract which performed by a T - shaped tube, left in the common bile duct for post-operative drainage.
10. Sailography.
It is a radiological contrast medium investigation for studying the salivary glands, main paratoid and sub-mandibular glands and their ducts.
11. Nasopharyngography.
It is a radiological contrast media investigation of nasopharynx and extent of lesion like carcinoma.
12. Dacrocystography.
It is a radiological contrast medium investigation which is used to studying the nasolacrimal duct system.
13. Bronchography.
It is a radiological contrast medium investigation of bronchial tree and mainly done for investigate peripheral tumours.
14. Mylography.
It is a radiological contrast media investigation of spinal cord to study the structural details of spinal cord, medullaris nerves and spinal canal. Nowadays, with the improvement of MRI technology, this procedure is rarely performed due to its various side-effects and complications.
15. Arthrography.
It is a radiological contrast medium investigation used to access bones and joints problem.
16. Shuntography.
It is a radio-nuclide scanning method for evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid shut patency. Radio-nuclide is used as contrast agent.
17. Cariotid Angiography.
It is a angiography used to demonstrate abnormalities and displacement of vessels to anterior and middle part of brain by using contrast agent.
18. Discography.
It is a radiological technique used to verify the presence and source of discogenic pain by using contrast medium.
19. Sinography.
It is a radiological contrast medium investigation of sinus tract. It is performed by injecting contrast agent in dural sinuses of the skull, an obstruction in the circulation of blood in said sinuses or jugular vein can be demonstrated.
20. Larynography.
It is a radiological contrast medium investigation used for detailed view of hypo-pharyngeal and laryngeal anatomy, by inserting of contrast agent in larynx. It is helpful in ruling out carcinoma.
21. Lymphangiography.
It is also know as Lymph Node Angiogram, is a radiographic contrast medium investigation to view lymphatic circulation and lymph nodes by injecting contrast agent.
There are some more special procedures, but rarely performed nowadays of modern advanced imaging modalities. However, under Section of Special Procedures of this blog, you can find all procedure content. If you want to write us, use comment section.










Comments
Post a Comment